 |
modbuspp
1.1.40
C++ wrapper for the libmodbus library
|
 |
modbuspp
1.1.40
C++ wrapper for the libmodbus library
|
#include <bufferedslave.h>
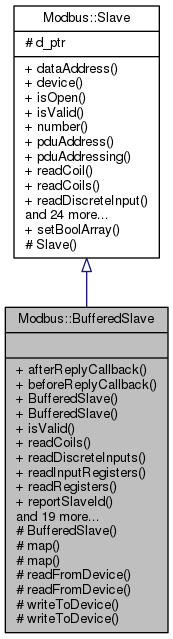
Public Member Functions | |
| Message::Callback | afterReplyCallback () const |
| Return the after reply callback function cb of this slave. | |
| Message::Callback | beforeReplyCallback () const |
| Return the before reply callback function cb of this slave. | |
| BufferedSlave (int slaveAddr, Device *dev=0) | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| BufferedSlave () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| int | dataAddress (int addr) const |
| returns the address in the MODBUS data model corresponding to a PDU address. More... | |
| Device * | device () const |
| returns the device used to access the network | |
| bool | isOpen () const |
| returns true if isValid() and device() is opened. | |
| bool | isValid () const |
| returns true if number() is sets | |
| int | number () const |
| Get slave number. More... | |
| int | pduAddress (int addr) const |
| returns the PDU address corresponding to an address in the MODBUS data model. More... | |
| bool | pduAddressing () const |
| Modbus addressing mode. More... | |
| int | readCoil (int addr, bool &dest) |
| Read a single coil (bit) More... | |
| virtual int | readCoils (int addr, bool *dest, int nb=1) |
| int | readDiscreteInput (int addr, bool &dest) |
| Read a single discrete input (input bit) More... | |
| virtual int | readDiscreteInputs (int addr, bool *dest, int nb=1) |
| int | readInputRegister (int addr, uint16_t &dest) |
| Read a single input register. More... | |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | readInputRegister (int addr, Data< T, e > &dest) |
| Read a single input data. More... | |
| virtual int | readInputRegisters (int addr, uint16_t *dest, int nb=1) |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | readInputRegisters (int addr, Data< T, e > *dest, int nb=1) |
| Read many input data. More... | |
| int | readRegister (int addr, uint16_t &dest) |
| Read a single register. More... | |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | readRegister (int addr, Data< T, e > &dest) |
| Read a single holding data. More... | |
| virtual int | readRegisters (int addr, uint16_t *dest, int nb=1) |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | readRegisters (int addr, Data< T, e > *dest, int nb=1) |
| Read many holding data. More... | |
| virtual int | reportSlaveId (uint16_t max_dest, uint8_t *dest) |
| template<typename T , Endian e = EndianBig> | |
| int | reportSlaveId (SlaveReport< T, e > &dest) |
| returns a description of the controller More... | |
| void | setAfterReplyCallback (Message::Callback cb) |
| Set the after reply callback function cb of this slave. More... | |
| void | setBeforeReplyCallback (Message::Callback cb) |
| Set the before reply callback function cb of this slave. More... | |
| int | setBlock (Table t, int nmemb, int startAddr=-1) |
| Setting a block of data in the memory map. More... | |
| void | setDevice (Device *dev) |
| Sets the device used to access the network. | |
| void | setNumber (int n) |
| Sets the slave number. | |
| void | setPduAddressing (bool pduAddressing=true) |
| Set the Modbus addressing mode. More... | |
| int | updateBlockFromSlave (Table t) |
| Update data block t from the real slave. More... | |
| bool | updateBlockFromSlave () |
| Update all data blocks from the real slave. More... | |
| int | updateSlaveFromBlock (Table t) |
| Update the real slave from data block t. More... | |
| bool | updateSlaveFromBlock () |
| Update the real slave from coils and holding registers data blocks. More... | |
| virtual int | writeCoil (int addr, bool src) |
| virtual int | writeCoils (int addr, const bool *src, int nb) |
| int | writeDiscreteInput (int addr, bool src) |
| Write a single discrete input (bit) More... | |
| int | writeDiscreteInputs (int addr, const bool *src, int nb) |
| Read many discrete inputs (bits) More... | |
| int | writeInputRegister (int addr, uint16_t value) |
| Write a single register. More... | |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | writeInputRegister (int addr, Data< T, e > &value) |
| Write a single input data. More... | |
| int | writeInputRegisters (int addr, const uint16_t *src, int nb) |
| Write many input registers. More... | |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | writeInputRegisters (int addr, Data< T, e > *src, int nb=1) |
| Write many input data. More... | |
| virtual int | writeReadRegisters (int write_addr, const uint16_t *src, int write_nb, int read_addr, uint16_t *dest, int read_nb) |
| virtual int | writeRegister (int addr, uint16_t value) |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | writeRegister (int addr, Data< T, e > &value) |
| Write a single holding data. More... | |
| virtual int | writeRegisters (int addr, const uint16_t *src, int nb) |
| template<typename T , Endian e> | |
| int | writeRegisters (int addr, Data< T, e > *src, int nb=1) |
| Write many holding data. More... | |
| virtual | ~BufferedSlave () |
| Destructor. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | setBoolArray (bool *dest, const uint8_t *src, size_t n) |
| Set many booleans from an array of bytes. More... | |
Buffered Slave.
| Modbus::BufferedSlave::BufferedSlave | ( | int | slaveAddr, |
| Device * | dev = 0 |
||
| ) |
Constructor.
Constructor of a new buffered slave with the slaveAddr identifier. If the device dev is provided, usually of the class Master and dev->isOpen() returns true:
| Modbus::BufferedSlave::BufferedSlave | ( | ) |
Default Constructor.
object cannot be used without calling setNumber()
Referenced by writeInputRegister().
|
inherited |
returns the address in the MODBUS data model corresponding to a PDU address.
If the PDU addressing mode is not enabled (which is the case by default), the data model address is equal to the PDU address plus 1, otherwise they are equal.
|
inherited |
Get slave number.
This function shall get the slave number.
|
inherited |
returns the PDU address corresponding to an address in the MODBUS data model.
If the PDU addressing mode is not enabled (which is the case by default), the PDU address is equal to the MODBUS address minus 1, otherwise they are equal.
|
inherited |
Modbus addressing mode.
This function shall return the Modbus addressing mode used. The address mode used is, by default, that of the data model, that is to say, a numbering of the registers from 1 to n.
The Modbus application protocol defines precisely PDU addressing rules. In a Modbus PDU each data is addressed from 0 to 65535.
It also defines clearly a Modbus data model composed of 4 blocks that comprises several elements numbered from 1 to n.
In the Modbus data Model each element within a data block is numbered from 1 to n.
Afterwards the Modbus data model has to be bound to the device application (IEC -61131 object, or other application model).
|
inlineinherited |
Read a single coil (bit)
This function shall read a signle bit (coil) to the address addr of the device. The result of reading is stored in dest as boolean.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x01 (read coil status).
References Modbus::Slave::readCoils().

|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
Read a single discrete input (input bit)
This function shall read a single input bits to the address addr of the device. The result of reading is stored in dest as boolean.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x02 (read input status).
References Modbus::Slave::readDiscreteInputs().
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
Read a single input register.
This function shall read a single input register to the address addr of the device.
The result of reading is stored in dest as word values (16 bits).
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x04 (read input registers). The holding registers and input registers have different historical meaning, but nowadays it's more common to use holding registers only.
References Modbus::Slave::readInputRegisters().
Referenced by writeInputRegister().
|
inlineinherited |
Read a single input data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall read a single input data to the address addr of the device.
The result of reading is stored in dest as T value.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x04 (read input registers).
References Modbus::Slave::readInputRegisters(), and Modbus::Data< T, e >::registers().
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
Read many input data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall read the content of the nb input data to the address addr of the device.
The result of reading is stored in dest array as T values.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x04 (read input registers).
References Modbus::Slave::readInputRegisters().
|
inlineinherited |
Read a single register.
This function shall read a signle holding register to the address addr of the device.
The result of reading is stored in dest as word values (16 bits).
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x03 (read holding registers).
References Modbus::Slave::readRegisters().
Referenced by writeInputRegister().

|
inlineinherited |
Read a single holding data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall read a single holding data to the address addr of the device.
The result of reading is stored in dest as T value.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x03 (read holding registers).
References Modbus::Slave::readRegisters(), and Modbus::Data< T, e >::registers().
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
Read many holding data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall read the content of the nb data to the address addr of the device.
The result of reading is stored in dest array as T values.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x03 (read holding registers).
References Modbus::Slave::readRegisters().

|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
returns a description of the controller
SlaveReport is a template class for storing and manipulate slave identifier datas returns by the MODBUS 17 function.
| dest | description of the controller |
References Modbus::Slave::reportSlaveId(), and Modbus::Slave::Slave().
| void Modbus::BufferedSlave::setAfterReplyCallback | ( | Message::Callback | cb | ) |
Set the after reply callback function cb of this slave.
This function is called after the main message manager responds to the master by sending it a response from the contents of the memory map.
| void Modbus::BufferedSlave::setBeforeReplyCallback | ( | Message::Callback | cb | ) |
Set the before reply callback function cb of this slave.
This function is called before the main message manager responds to the master by sending it a response from the contents of the memory map.
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::setBlock | ( | Table | t, |
| int | nmemb, | ||
| int | startAddr = -1 |
||
| ) |
Setting a block of data in the memory map.
A single block of type t can be defined for a given slave. The block has nmeb elements and starts at startAddr.
|
staticinherited |
Set many booleans from an array of bytes.
All the bits of the bytes read from the first position of the array src are written as booleans in the dest array.
| dest | |
| src | |
| n |
Referenced by Modbus::Slave::writeRegister().

|
inherited |
Set the Modbus addressing mode.
| pduAddressing | true for Modbus PDU adressing |
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::updateBlockFromSlave | ( | Table | t | ) |
Update data block t from the real slave.
| bool Modbus::BufferedSlave::updateBlockFromSlave | ( | ) |
Update all data blocks from the real slave.
Referenced by writeInputRegister().
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::updateSlaveFromBlock | ( | Table | t | ) |
Update the real slave from data block t.
| bool Modbus::BufferedSlave::updateSlaveFromBlock | ( | ) |
Update the real slave from coils and holding registers data blocks.
Referenced by writeInputRegister().
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::writeDiscreteInput | ( | int | addr, |
| bool | src | ||
| ) |
Write a single discrete input (bit)
This function shall write the status of src at the address addr of the memory map.
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::writeDiscreteInputs | ( | int | addr, |
| const bool * | src, | ||
| int | nb | ||
| ) |
Read many discrete inputs (bits)
This function shall read the status of the nb bits (input) to the address addr of the memory map. The result of reading is stored in dest array as boolean.
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::writeInputRegister | ( | int | addr, |
| uint16_t | value | ||
| ) |
Write a single register.
This function shall write the value of value input register at the address addr of the memory map.
|
inline |
Write a single input data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall write a single input data from value at address addr of the device.
References BufferedSlave(), Modbus::Slave::readInputRegister(), Modbus::Slave::readInputRegisters(), Modbus::Slave::readRegister(), Modbus::Slave::readRegisters(), Modbus::Data< T, e >::registers(), Modbus::Slave::reportSlaveId(), updateBlockFromSlave(), updateSlaveFromBlock(), writeInputRegisters(), Modbus::Slave::writeRegister(), and Modbus::Slave::writeRegisters().
| int Modbus::BufferedSlave::writeInputRegisters | ( | int | addr, |
| const uint16_t * | src, | ||
| int | nb | ||
| ) |
Write many input registers.
This function shall write the content of the nb input registers from the array src at address addr of the memory map.
Referenced by writeInputRegister(), and writeInputRegisters().
|
inline |
Write many input data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall write the content of the nb input data from the array src at address addr of the memory map.
References writeInputRegisters().
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
Write a single holding data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall write a single holding data from value at address addr of the device.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x10 (preset multiple registers).
References Modbus::Data< T, e >::registers(), Modbus::Slave::reportSlaveId(), Modbus::Slave::setBoolArray(), and Modbus::Slave::writeRegisters().
|
virtual |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Reimplemented from Modbus::Slave.
|
inlineinherited |
Write many holding data.
Data is a template class for storing, transmitting, and receiving arithmetic data in multiple 16-bit Modbus registers.
This function shall write the content of the nb holding data from the array src at address addr of the device.
The function uses the Modbus function code 0x10 (preset multiple registers).
References Modbus::Slave::writeRegisters().
